sábado, 13 de septiembre de 2008
F-35. PUSH THE LIMIT.
URALVAGONZAVOD T-90 TANK.
US MARINES CORPS




WINDS OF WAR
 A U.S. Air Force F-16 Fighting Falcon aircraft sits on a trim pad before an engine run up at Joint Base Balad, Iraq, July 16, 2008. U.S. Air Force photo by Senior Airman Julianne Showalter
A U.S. Air Force F-16 Fighting Falcon aircraft sits on a trim pad before an engine run up at Joint Base Balad, Iraq, July 16, 2008. U.S. Air Force photo by Senior Airman Julianne Showalter


LOS PRIMEROS COMBATES..

Ofensiva alemana.
Se lanzan ataques aéreos sobre las unidades del otro lado del frente, en acciòn se lanzan los bombarderos en picado Junkers 87 causando bajas importantes.Misiones de bombardeo de altura sobre las fuerzas republicanas ubicadas al este en Caldens, se divisan dos unidades españolas y son masacradas desde el aire.
Maniobras de reconocimiento en terreno republicano, se divisan 3 batallones de infanteria. A continuaciòn se realiza el ataque de la artilleria de campaña y bombardeo de Junkers 87 ocasionando bajas importantes. Se toma Bufalvent por un batallòn de panzers. Se destruye una unidad española en caldens.
Ofensiva española.
Se sucede el ataque principalmente de artilleria en todo el frente causando grandes bajas en el 1er btn de panzers. El resto del escenario sin novedades significantes.
Dia 2
Ofensiva alemana.
Intento alemán de bombardeo en picado pero la flota es abatida por la defensa aérea.
Se realiza un ataque sobre las baterias AA españolas. dos misiones debilitan las unidades de defensa. A continuación se retira del frente el 1er btn de panzer de Bufalvent. se solicitan refuerzos para esta unidad. Se rompe el frente en la ciudad que abre el frente de batalla. 9 unidades españolas de infanteria son destruidas hasta ahora agregandose tambièn a 2de artilleriade campaña. La aviacion de caza alemana derriba una unidad aèrea española. Se suministra otra flota de Junkers 87B para sustituir la unidad perdida al frente.
Ofensiva española.
Otra unidad aèrea española es destruida por las defensas AA alemanas. No se realizan màs ataques de las tropas republicanas.
viernes, 12 de septiembre de 2008
THE SPECIAL UNITS WAFFEN SS

Of all the German military organizations of WWII the Waffen-SS is one of the most widely studied. This is in part because of the combat record of the Waffen-SS and the elite status of many of its units, and in part because of the brutality attributed to some of its formations and the war crimes some of its members were responsible for.
By the end of WWII over 1,000,000 soldiers in 38 divisions would serve in the Waffen-SS, including over 200,000 conscripts.The Waffen-SS was a part of the German Schutzstaffel or SS, which saw its rise during the late 1920s and early 1930s.
The SS was the single most powerful political organization within the Third Reich and consisted of the Allgemeine-SS, Totenkopfverbande, and the Waffen-SS.The Waffen-SS was born in 1933 after Hitler came to power when Politisches Bereitschaften or Political Readiness Detachments were formed under the control of the SS. These units were organized along military lines and were intended to help counter Communist strikes. On October 1st, 1934 these units became the SS-Verfügungstruppen or SS Special Use Troops. Initially the Verfügungstruppen consisted of small detachments located in larger German cities but by 1935 they were organized into battalions and in 1936 into Standarten or regiments. In 1936 two main SS-V Standarten existed, Deutschland and Germania.
The Leibstandarte Adolf Hitler also existed at this time and although related it was considered somewhat outside the purview of the SS-V.In 1938 the SS-Verfügungstruppen took part in the occupation of Austria and Czechoslovakia along side the Wehrmacht. After the occupation of Austria a third Standart was formed known as Der Führer. In 1939 the SS-Verfügungstruppen consisted of three Standarden, the LAH, and a number of smaller service and support units. For the Campaign in Poland in 1939 all SS-V units were organized into the SS-Verfügungstruppe-Division and placed under the operational command of the Wehrmacht. The SS-Verfügungstruppe-Division also fought in the Western Campaign 1940. After the conclusion of the Western Campaign the SS-Verfügungstruppen was renamed and became the Waffen-SS.Although the Waffen-SS is frequently considered an elite organization not all of its units were actually elite. Some Waffen-SS units formed after 1943 had less than ideal combat records. This was in part due to the fact that the number of volunteers eligible for service in the Waffen-SS shrank as the war continued while the need for replacements increased. The number of conscripts taken into the Waffen-SS of lesser quality or questionable ability had a direct impact on combat effectiveness.
After WWII ended the Waffen-SS was condemned at the Nurnberg Trials as a criminal organization. This was in part due to a series of high profile atrocities and because of their connection to the SS and NSDAP. Only those who were conscripted into the Waffen-SS were exempt from the Nurnberg declaration. As a result Waffen-SS veterans were generally denied the rights and benefits granted to other WWII German veterans. Waffen-SS prisoners of war were often held in strict confinement and were treated harshly by the Soviets. Many foreign volunteers that served in the Waffen-SS were also treated severely by their national governments. In the years since WWII there have been attempts to rehabilitate the image and legality of Waffen-SS veterans, both through legislation and in published works by former officers like Paul Hausser (Soldaten wie andere auch - Soldiers Like Any Other). To this day the stigma on veterans from the Waffen-SS remains.
LA GUERRA CIVIL ESPAÑOLA. 1936

Alemania ayudó a Franco enviando a España la Legión Cóndor, y miles de técnicos y asesores militares.Aprovechó la guerra para probar sus nuevos modelos de armas y tácticas. Se probaron los cazas Messerschmitt Bf 109 Junkers Ju 87 A/B y los bombarderos Junkers Ju 52 y Heinkel He 111.Estrenó en España sus tácticas de bombardeo sobre ciudades. Aunque no fue el único, el más famoso fue el bombardeo de Guernica representado por Picasso en su cuadro Guernica, expuesto en el pabellón español de la Exposición Universal de París de 1937.La Legión hizo su último desfile oficial en España el 22 de mayo de 1939, cuatro días después 5.136 oficiales y soldados alemanes salieron por barco para Alemania, llevándose con ellos unas 700 toneladas de equipo y la mayor parte de los aviones que quedaban. Desde su llegada a España en julio de 1936 habían reivindicado la destrucción de 386 aviones enemigos (313 de ellos en combate aéreo), con la pérdida de 232 de los suyos (de los cuales sólo 72 fueron destruidos por la acción enemiga). Además, los aviones de la Legión Cóndor habían lanzado unas 21.000 toneladas de bombas, contribuyendo en no escasa medida a la victoria final de los nacionales. 226 miembros de la Legión perdieron la vida en España.

Escenario: Barcelona.
turnos totales - 21
victoria brillante - 14 turnos
victoria - 16 turnos.
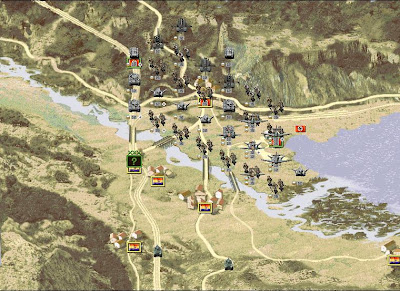
Las fuerzas terrestres se componen por 12 batallones de infanteria, 2 batallones de ingenieros, seis batallones de artilleria pesada,2 batallones de tropa de reconocimiento, 2 seciones de defensa aèrea, dos secciones de cañones antitanques y cuatro batallones de tanques Pz IIIC.

El plan estratègico alemán consiste en dividir sus fuerzas en tres lineas de ataque. para tratar de cercar el terreno republicano hacia el sur tomando las ciudades en el camino principal a Barcelona. Es indispensable utilizar al màximo la ventaja aèrea e iniciar los ataques con fuego de artillerìa sobre las unidades visibles en un previo reconocimiento.





















































